Turbulent Channel Flow Cheat Sheet - Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental.
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia.
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia.
Turbulence in OpenChannel Flows PDF
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. The.
DNS Turbulent channel flow DNS Database
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed.
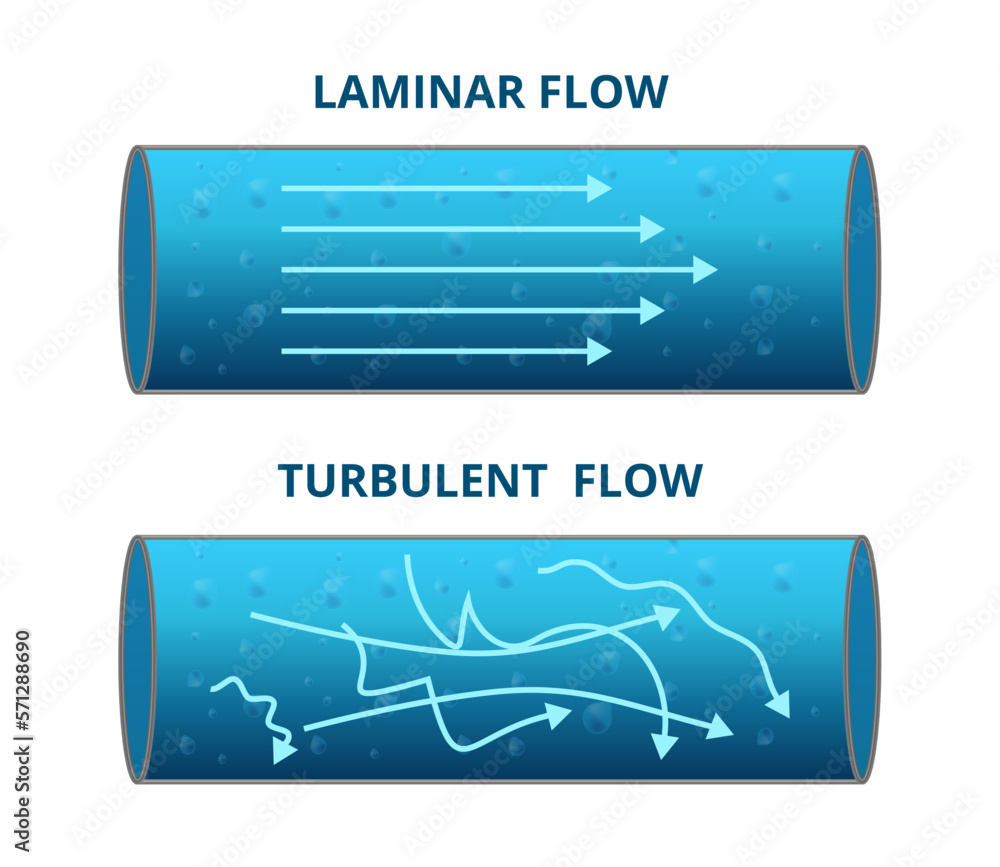
Vector scientific illustration of laminar flow and turbulent flow
Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be.
Laminar flow and turbulent flow diagram. Royalty Free Stock Vector
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. The.
Advantages of Turbulent Flow EngineerExcel
Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity).
Laminar And Turbulent Flow Diagrams Flow Turbulent Laminar C
Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed.
Periodic turbulent channel flow — v4.1322geae4400
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. Critical.
Home [www.mtfc.uliege.be]
The ratio of inertial to viscous. Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and.
Turbulent channel flow the instantaneous Qcriterion isosurfaces with
Critical flow occurs when the velocity of water is the same as the speed at which disturbances of the free surface will move through shallow. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also.
2 Laminar versus turbulent flow. Turbulent flow, which occurs at high
Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia. Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. Critical.
Critical Flow Occurs When The Velocity Of Water Is The Same As The Speed At Which Disturbances Of The Free Surface Will Move Through Shallow.
Part i provides a general introduction to turbulent flows, how they behave, how they can be described quantitatively, and the fundamental. Engineers study flow in reservoirs, pipes, water and waste water treatment, and building ventilation, and also river flooding, groundwater. The ratio of inertial to viscous. Whether a flow is laminar or turbulent depends of the relative importance of fluid friction (viscosity) and flow inertia.






![Home [www.mtfc.uliege.be]](https://www.mtfc.uliege.be/upload/docs/image/jpeg/2019-11/turbulent_channel_flow.jpg.associated/th-1920x0-turbulent_channel_flow.jpg.jpg)
