An Infinite Sheet Of Charge With Charge Density - Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. A charge of +q is fixed in space. Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane.
An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. A charge of +q is fixed in space. Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q.
Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. A charge of +q is fixed in space.
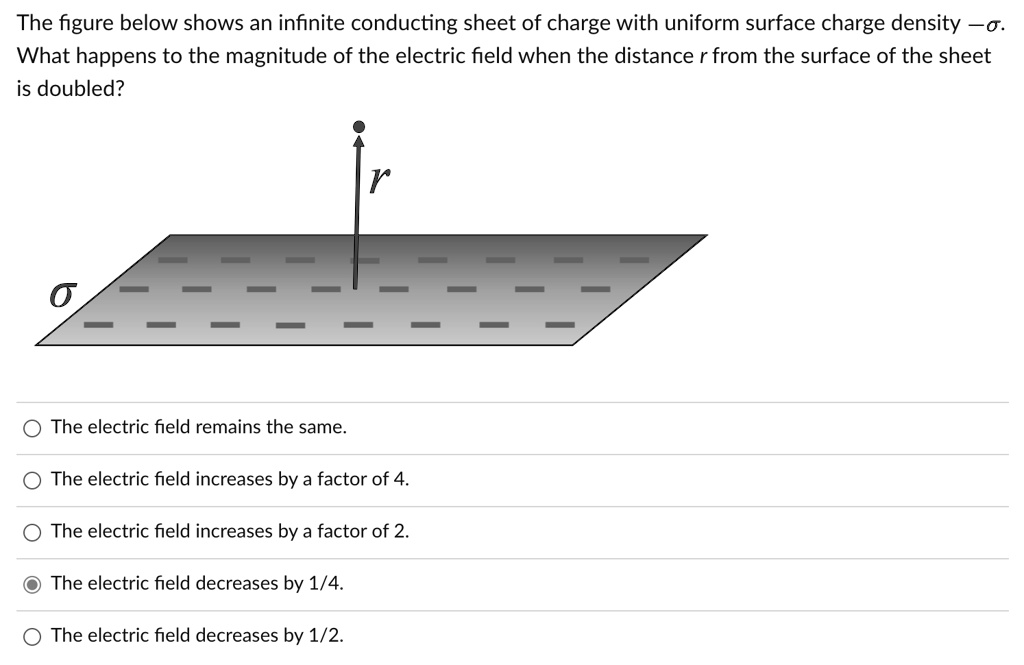
the figure below shows an infinite conducting sheet of charge with
An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. Then it was moved.
A particle A of charge a placed near a uniformly charged infinite plane
Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c /.
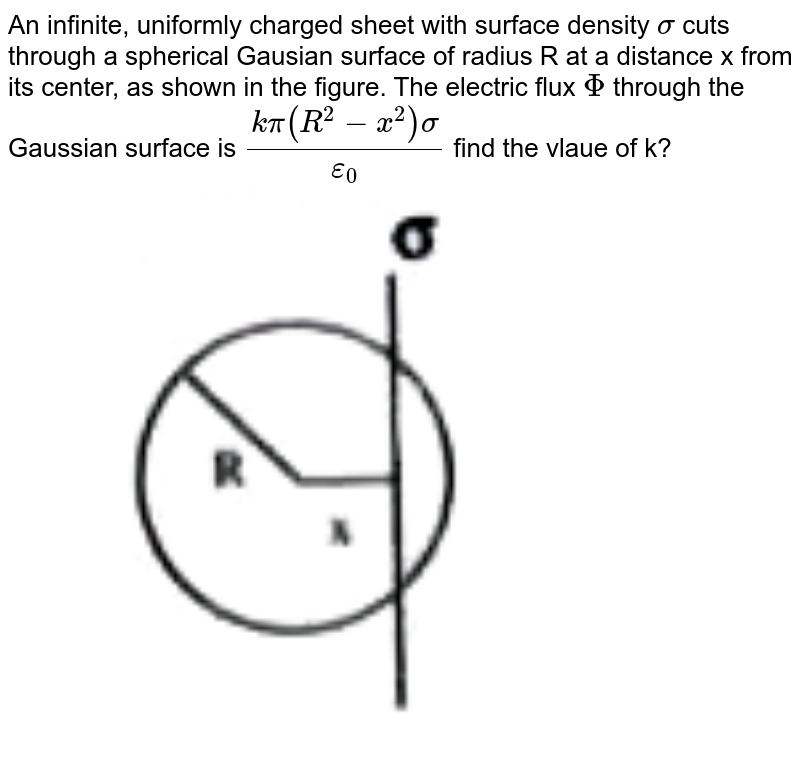
An infinite, uniformly charged sheet with surface charge density (p
A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A charge of +q is.
Let σ be the uniform surface charge density of two infinite thin plane
A charge of +q is fixed in space. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y.
For the infinite charged sheet case (a) A sketch of the charge density
A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c /.
A particle A of charge q placed near a uniformly charged infinite plane
Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. Since, we have the surface.
An infinite uniformly charged sheet with surface charge density σ
An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. A charge of +q.
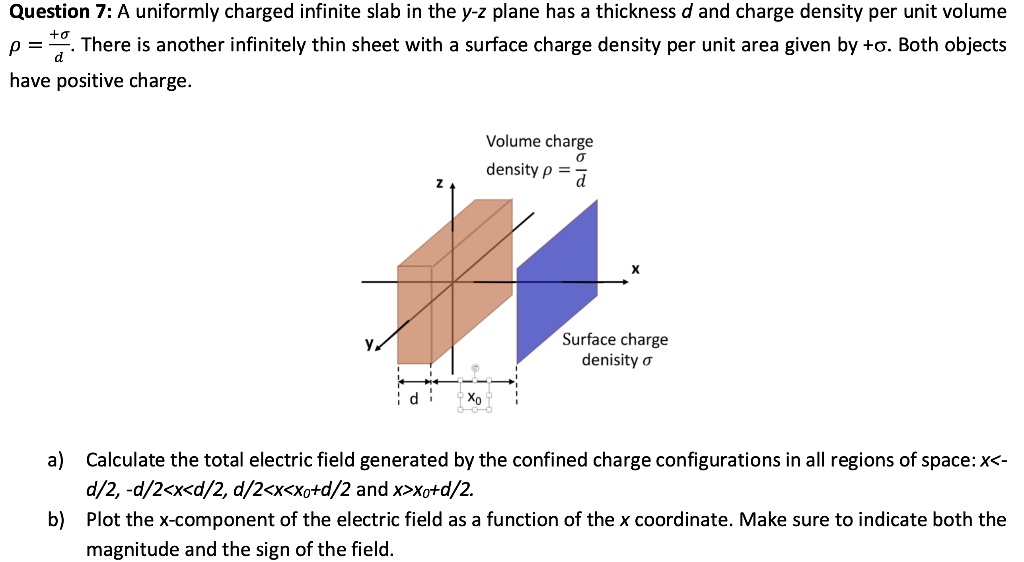
SOLVED Question 7 A uniformly charged infinite slab in the Vz plane
A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. Then it was moved along a straight line to a. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. A charge of +q is.
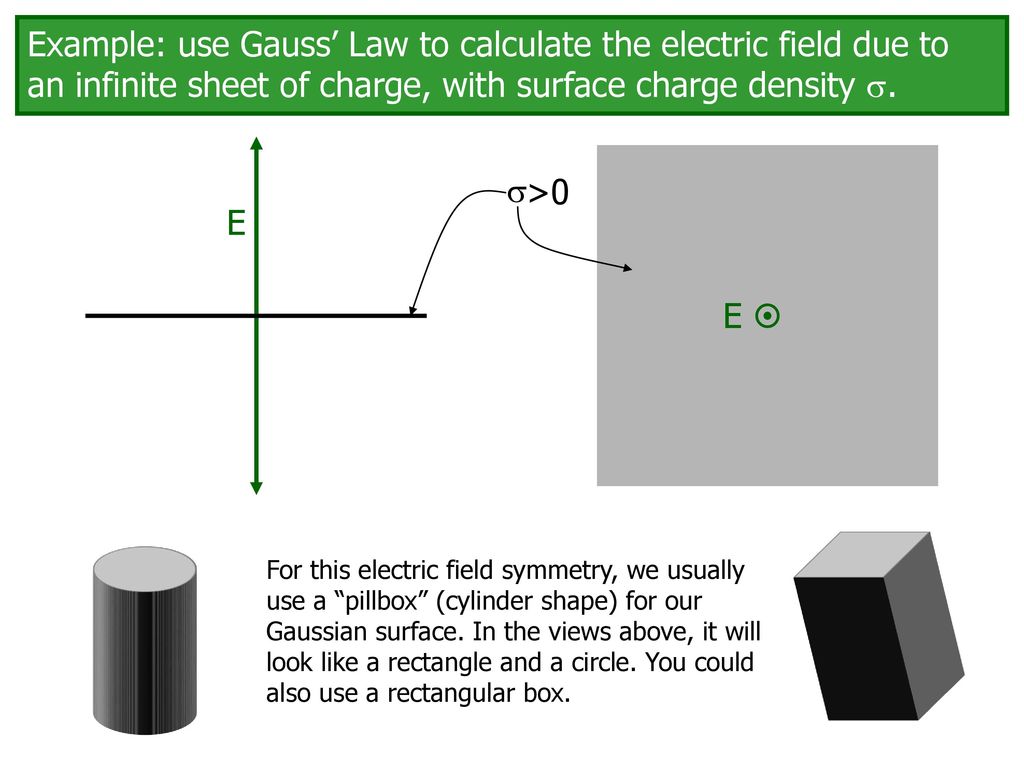
Example use Gauss’ Law to calculate the electric field due to an
Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A charge of +q is fixed in space. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside.
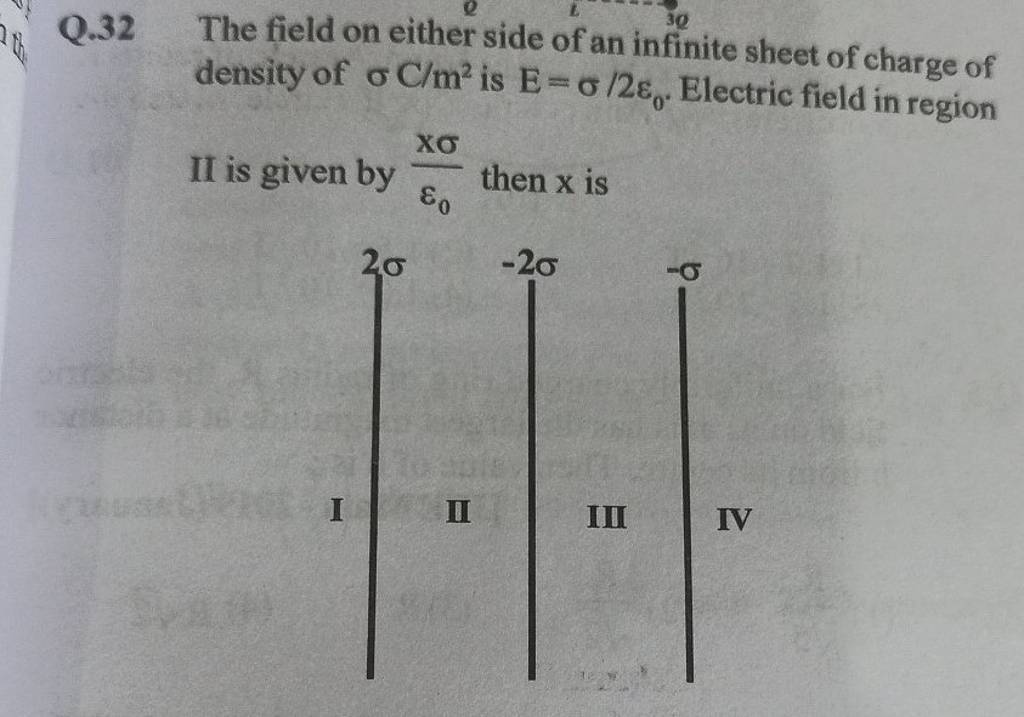
Q.32 The field on either side of an infinite sheet of charge of density o..
Then it was moved along a straight line to a. Since, we have the surface charge density, we can find the total charge enclosed by the surface by finding the area of the charged sheet inside the. A charge of +q is fixed in space. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from.
Since, We Have The Surface Charge Density, We Can Find The Total Charge Enclosed By The Surface By Finding The Area Of The Charged Sheet Inside The.
Then it was moved along a straight line to a. A second charge of +q was first placed at a distance r 1 away from +q. An infinite plane sheet of charge having uniform surface charge density +σsc/m2 + σ s c / m 2 is placed on x − y x − y plane. A charge of +q is fixed in space.